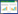文章信息
基金项目
- 广东省乡村振兴战略专项资金种业振兴项目(2022-XPY-00-001)
作者简介
- 姜维伦(1999—),男,在读硕士生,研究方向为猪遗传分子育种,E-mail:13725290517@163.com.
通讯作者
- 何祖勇(1981—),男,博士,副教授,研究方向为猪生物育种,E-mail:zuyonghe@foxmail.com.
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2023-06-26
2. 广东壹号食品股份有限公司,广东 广州 510620
2. Guangdong Yihao Food Co. Ltd., Guangzhou 510620, China
【研究意义】猪的椎骨由颈椎、胸椎、腰椎、荐椎和尾椎组成,其中猪颈椎、荐椎和尾椎数变化很小,颈椎数多为7个(颈椎数只有5个和6个的猪仅各发现1头[1-2]),荐椎数为4个,尾椎数为20~23个。胸腰椎数在猪品种间存在数量差异,欧洲商品猪种的胸腰椎数可达21~23个,而我国地方猪种的胸腰椎数只有19~20个[3]。研究表明,增加1个胸椎可使猪胴体长增加80 mm[4],同时椎骨数增加使得背最长肌增长和腹腔容积增大[5]。此外,胸椎数决定了肋骨对数。猪肋骨俗称排骨,因肉质鲜嫩口感好,肋排成为猪身上售价比较贵的部位,因此通过分子标记辅助选择肋骨对数较多的家猪个体,培育高肋骨数的新品系,可以提高生猪养殖企业的经济效益[6]。【前人研究进展】在猪中已发现2个与椎骨数量有关联的QTL位点,分别位于1号[7]和7号染色体[8]。1号染色体上的核受体亚家族6 A组成员1(Nuclear receptor subfamily 6 group A member 1,NR6A1)基因被认为是与猪椎骨数相关的候选基因[9-10]。7号染色体上与椎骨数量相关的QTL位点被定位在椎骨发育相关(Vertebrae development associated,VRTN)基因上[11]。VRTN是调控胸椎发育的关键基因,其表达产物VRTN蛋白是定位于细胞核中的一种新型转录因子,VRTN基因纯合敲除小鼠具有胚胎致死效应,而杂合子小鼠脊柱发育异常且胸椎数显著低于野生型小鼠[12]。前人研究发现,猪VRTN基因含有2个影响胸椎数的因果突变位点,第1个突变在7号染色体上第20 311个碱基后插入1个291 bp的DNA片段(g.20311_20312ins291),该插入突变位于VRTN基因内含子1,在大白猪中单个g.20311_20312ins291等位基因可增加0.55~0.60个胸椎数[13]。第2个突变是第19 034个碱基由腺嘌呤替换成胞嘧啶(g.19034A > C),该点突变位于VRTN的启动子区[14]。这两种突变均位于VRTN基因保守的功能元件中,因此推测这两种突变可能通过改变VRTN表达来影响胸椎数。【本研究切入点】由于已有研究证实VRTN基因中两个突变均可影响猪的胸椎数,因此本研究以两广小花猪为研究群体,在VRTN基因PCR扩增测序结果的基础上,对胴体性状和肉质性状进行相关分析。【拟解决的关键问题】鉴定两广小花猪群体中VRTN基因的突变情况并探究VRTN基因突变对两广小花猪胸椎数及胴体性状与肉质性状的影响,以期为两广小花猪的分子育种提供参考。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料1.1.1 试验动物 供试两广小花猪69头,均由广东壹号食品股份有限公司提供。2021年9月17日采集每头猪右耳末端的耳组织,现场取样后经生理盐水洗净,储存在含有75%乙醇的1.5 mL离心管中,直接提取基因组或置于-20 ℃下保存、备用。上述69头两广小花猪分别于2021年9月17日、29日在广州孔旺记食品有限公司屠宰,屠宰时猪达339~367日龄。
1.1.2 主要试剂 基因组提取试剂盒OMEGA Tissue DNA Kit D3396、TA克隆pMD19-T Vector Cloning Kit和TaKaRa DL1000 DNA Marker,购于广州安邦生物科技有限公司;Genstar 2×Taq PCR StarMix with Loading Dye,购于广州美仑生物科技有限公司;东盛100 bp ladder,购于广州慧恒生物科技有限公司;SYBR-Green I核酸染料,购于北京普博欣生物科技有限责任公司。
1.1.3 主要仪器 RH-1000肉品系水力测定仪,购于广州润湖仪器有限公司;手提式多功能色差仪NR60CP+,购于深圳市三恩时科技有限公司;C-LM3B型数显式肌肉嫩度仪,购于北京天翔飞域科技有限公司;胴体肌肉pH值测定仪pH-STAR,购于北京布拉德科技发展有限公司。
1.2 试验方法1.2.1 基因组提取 采用基因组提取试剂盒抽提DNA样品,并使用超微量分光光度计测定DNA的浓度与纯度,存放于-20 ℃冰箱中备用。
1.2.2 引物设计 参考NCBI中的VRTN基因序列(Gene ID: 100157734),使用Primer3在线网站设计VRTN基因检测引物(表 1),并由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成。
1.2.3 PCR反应体系和反应程序 PCR反应体系:模板DNA总量为200~300 ng,上下游引物各1.5 μL(10 pmol/μL),2×Taq PCR Mix 15 μL,补充ddH2O至30 μL。PCR反应程序:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃变性30 s、65 ℃退火30 s、72 ℃延伸45 s,35个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min。10 μL PCR产物使用1.5%琼脂糖凝胶进行电泳检测。
1.2.4 TA克隆 PCR产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳后进行切胶回收,将胶回收产物与PMD19载体进行TA克隆与转化,反应体系:胶回收产物3 μL、SolutionⅠ5 μL、PMD19载体1 μL,加ddH2O至10 μL。反应程序:16 ℃连接4 h。之后进行转化,将10 μL连接产物与35 μL感受态DH5α混合,在冰上放置30 min后,42 ℃热激45 s,冰上放置2 min,加入500 μL无抗液体LB培养基,37 ℃下220 r/min摇菌1 h后,使用30 μL含有氨苄的固体培养基进行涂布,12~15 h后挑取单克隆测序。
1.2.5 菌种测序和序列分析 将单克隆送由上海生工生物工程股份有限公司测序。测序结果使用SnapGene 4.36软件进行序列比对,检测遗传变异位点;使用Chromas 2.56软件查看测序结果峰图,确认突变碱基类型。
1.2.6 猪胴体性状和肉质性状测定 两广小花猪屠宰前禁饲24 h,宰前8 h禁水。在屠宰现场宰杀后放血、过热水、刮毛、去除头和内脏(板油和肾脏除外),之后将猪从头到尾沿中线切开。胴体性状测定方法参照文献[15]。肉质性状测定包括猪背最长肌肉色、pH值、剪切力和失水率。从两广小花猪左半边胴体倒数第三根肋骨处到最后一根肋骨处切断背最长肌,以背最长肌进行肉色性状测定,肉色使用Lab颜色模式表示,L代表明度,a代表红绿色,b代表黄蓝色,测定方法参照文献[16-18]。
采用GraphPad Prism 9.0统计软件进行t检验,比较分析数据差异显著性。
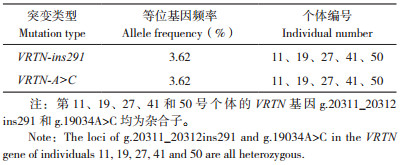
2 结果与分析 2.1 两广小花猪VRTN基因型分析2.1.1 VRTN基因g.20311_20312ins291突变鉴定结果 利用引物VRTN-ins291-F和VRTN-ins291-R对69头两广小花猪覆盖VRTN基因g.20311_20312ins291的区域进行PCR扩增,通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测PCR产物。结果(图 1)显示,有5个个体(第11、19、27、41、50号)可扩增出411 bp的插入型条带和120 bp的野生型条带,说明这5个个体为携带VRTN基因g.20311_20312ins291突变的杂合子。
|
| M:Marker, NC:阴性对照 M: Marker, NC: Negative control 图 1 VRTN基因g.20311.20312 ins 291突变的PCR产物电泳结果 Fig. 1 Electrophoresis result of PCR product of VRTN gene with the g.20311.20312 ins 291 mutaion |
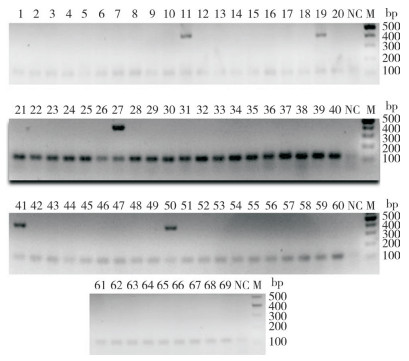
2.1.2 VRTN基因g.19034A > C突变鉴定结果 利用引物VRTN-A > C-F和VRTN-A > C-R对69头两广小花猪VRTN基因进行PCR扩增,PCR扩增产物经凝胶电泳分离和纯化后进行DNA测序。经序列比对分析发现,第11、19、27、41、50号两广小花猪的VRTN基因g.19034位点发生A > C突变(图 2)。

|
| 红色框代表VRTN基因的g.19034A > C位点,红色箭头为发生A > C突变个体 The red box represents the g.19034A > C locus of VRTN gene, and the red arrow represents individuals with A > C mutation 图 2 69头两广小花猪VRTN基因g.19034A > C序列比对结果 Fig. 2 Sequence alignment result of VRTN gene g.19034A > C sequence among 69 Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs |
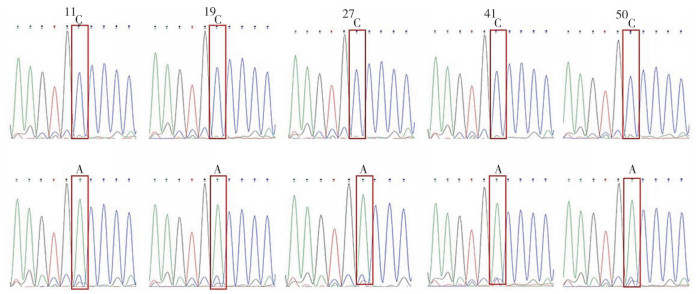
为进一步了解上述5个个体VRTN基因g.19034位点的纯合与杂合状态,PCR产物被克隆到T载体后,挑选多个克隆进行测序分析,结果(图 3)显示,这5个个体VRTN基因g.19034位点均存在A和C两种碱基,即它们均为杂合子。
|
| 图 3 VRTN基因g.19034A > C位点测序Chromas图谱分析 Fig. 3 Chromas map analysis of VRTN gene g.19034A > C locus sequencing |
2.1.3 VRTN基因突变频率 对69头两广小花猪的VRTN基因g.20311_20312ins291和g.19034A > C两种突变进行统计,结果(表 2)显示,g.20311_20312ins291和g.19034A > C两种突变的频率均为3.62%,且每个突变个体均含有这两种突变,推测这两种突变可能紧密连锁。
2.2 两广小花猪VRTN基因型与性状关联分析
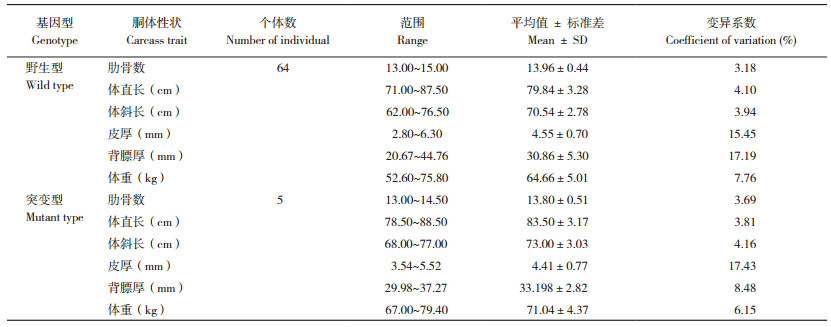
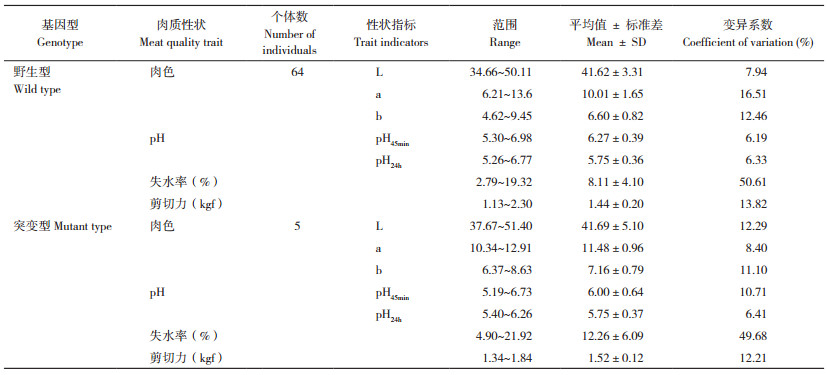
2.2.1 胴体性状与肉质性状测定结果 为分析VRTN突变是否对两广小花猪的肋骨数等胴体性状和肉质性状产生影响,本研究测量了供试69头两广小花猪的胴体性状与肉质性状。胴体性状测定结果(表 3)显示,突变型猪的体直长、体斜长、背膘厚和体重高于野生型,而肋骨数和皮厚低于野生型。肉质性状测定结果(表 4)显示,突变型猪背肌肉色明度L值、色度指数a值和b值、失水率和剪切力均高于野生型,而pH45 min和pH24 h均低于野生型。
|
|
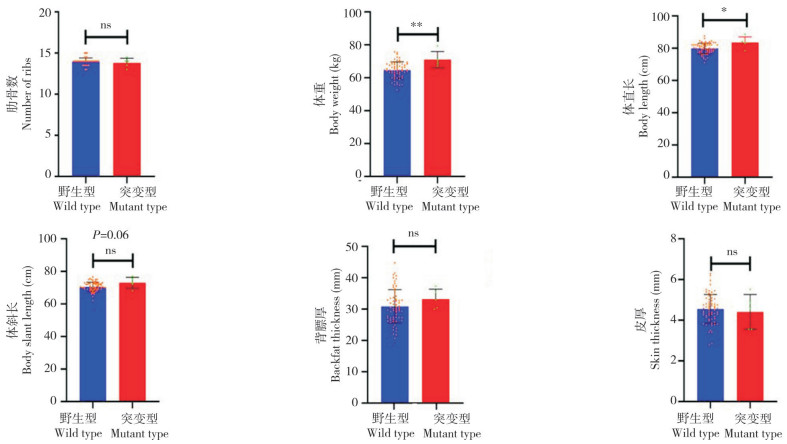
2.2.2 VRTN基因突变与胴体性状的相关性 统计分析结果(图 4)显示,VRTN基因杂合突变并不能显著提高两广小花猪的的肋骨数,但使猪体直长和体重分别显著增加4.6%和9.6%,体斜长增加3.5%、但差异不显著。此外,VRTN基因杂合突变分别增加6.5%的背膘厚和减少3.7%的皮厚,但两种基因型的背膘厚和皮厚均无显著性差异。结果表明VRTN突变可对两广小花猪的胴体性状产生有利影响。
|
| *:P < 0.05,**:P < 0.001 图 4 Student-t检验检测不同种VRTN基因型的两广小花猪胴体性状差异 Fig. 4 Student-t test for detecting differences in carcass traits between different VRTN genotypes in Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs |

|
| *:P < 0.05 图 5 Student-t检验检测不同种VRTN基因型的两广小花猪肉质性状差异 Fig. 5 Student-t test for detecting differences in meat quality traits between different VRTN genotypes in Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs |
2.2.3 VRTN基因突变与肉质性状的相关性 对于两种基因型背最长肌的肉质性状进行统计分析,结果显示VRTN基因杂合子肉色的L值相较于野生型增加0.01%、a值增加14.7%、b值增加8.4%,但结果没有显著影响;剪切力和pH值方面,两种基因型无显著性差异。失水率方面,VRTN基因杂合突变个体的失水率显著增加51.2%。
3 讨论广东是我国生猪生产的关键省份之一[19-20],选育本土猪种两广小花猪是广东生猪产业发展任务之一。猪胸椎数在畜牧业中是重要性状且具有高遗传力[21]。VRTN基因突变被证实与欧洲商品猪种的胸椎数量增多相关,同时还与胴体长度和乳头数量增多相关[22]。目前,有关VRTN基因的生物学功能研究较少。张慧[23]认为VRTN基因作为一种新型转录因子,在猪细胞核内表达同时选择性结合DNA基序来影响邻近基因的转录水平,并且VRTN基因可能通过NOTCH通路调控体节发育。影响欧洲商品猪胸椎数量的VRTN突变主要是插入突变g.20311_20312ins291和点突变g.19034A > C[24],这两种突变如何影响猪胸椎数量尚未清楚阐明。由于两种突变在两广小花猪中并未得到证实,因此本研究在69头两广小花猪中开展突变检测,结果发现5头猪中同时携带g.20311_20312ins291和g.19034A > C两种突变,且两个突变位点均为杂合子状态,因此这两个突变位点在两广小花猪中可能完全连锁,这与范寅[25]在苏太群体和杜长大商业群体中的研究结果一致。本研究发现VRTN基因杂合突变并不影响两广小花猪的肋骨数,这与Jiang等[26]在我国本土苏淮猪和Nakano等[27]在杜洛克猪中的研究结果不同,可能由于品种间遗传背景有差异。推测VRTN基因纯合突变可能会显著增加肋骨数而杂合突变不能改变两广小花猪的肋骨数。Huang等[28]在PIC猪的VRTN g.20311_20312ins291杂合子组中发现1头只有13根肋骨的猪,而野生型组和纯合突变组中的猪肋骨数均多于13根。此外,也可能是两广小花猪中存在其他影响肋骨数的候选基因。Zhang等[29]在大白猪与东北民猪杂交后代中发现7号染色体上存在多个影响猪肋骨数量的SNP,并且这些SNP对于猪肋骨的影响显著高于点突变g.19034A > C。VRTN基因纯合突变是否可以增加肋骨数有待配种获得纯合子群体后作进一步分析。虽然VRTN基因杂合突变不影响肋骨数,但却能增加体斜长、显著增加体直长和体重,该结果与Huang等[28]在PIC猪和Li等[30]在山下黑猪和鲁莱黑猪的研究结果类似。VRTN基因杂合突变对两广小花猪背膘厚虽然有6.5%的提升但无显著性差异,有研究表明VRTN基因突变不会影响苏淮猪和长白猪的背膘厚[26, 31],但Hirose等[22]研究发现VRTN突变与杜洛克猪肌内脂肪含量显著相关。一般来说,背膘厚与肌内脂肪含量呈正相关关系,因此VRTN基因可能是提高肌内脂肪含量的候选基因。肉质性状方面,VRTN基因杂合突变不改变背最长肌大部分的肉质性状,但会显著增加失水率,可能对肉质产生不利影响。有意思的是,杂合子肉色的a值提升14.7%,a值越高,则肉色越偏红,表明VRTN基因杂合突变可能会导致肉色更红,而要进一步研究VRTN基因对肉色的影响,可能需要更多的研究和数据支持。综上所述,VRTN基因突变会改善胴体性状,但对肉质带来不利影响。因此,如果以VRTN进行分子标记辅助选育两广小花猪,应考虑突变对胴体与肉质性状两者影响之间的平衡。
4 结论本研究对69头两广小花猪进行VRTN基因突变检测,结果发现,有5头猪为VRTN基因插入突变(g.20311_20312ins291)和点突变(g.19034A > C)的杂合子,其他个体没有发现这两种突变,表明这两种突变可能紧密联锁,它们的突变频率均为3.62%。对VRTN基因两种基因型的两广小花猪胴体性状与肉质性状进行研究,结果表明两种基因型肋骨数无显著差异,杂合子的体直长和体重分别显著提高4.6%和9.6%,体斜长提高3.5%但差异不显著,而两种基因型的背膘厚和皮厚无显著差异,说明VRTN基因突变对于胴体性状有益。而在背最长肌的肉质性状中,两种基因型只有失水率和肉色a值分别达到和接近显著性差异,其中VRTN基因杂合子的失水率提升51.2%、a值提升14.7%,说明VRTN基因突变可能会对肉质性状产生不利影响。后续研究需要权衡VRTN基因突变对于两广小花猪的肉质与胴体性状的影响,为两广小花猪的分子标记辅助遗传改良提供参考。
| [1] |
KING J W B, ROBERTS R C. Carcass length in the bacon pig; its association with vertebrae numbers and prediction from radiographs of the young pig[J]. Animal Production, 1960, 2(1): 59-65. DOI:10.1017/s0003356100033493 |
| [2] |
BERGE S. Genetical researches on the number of vertebrae in the pig[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 1948, 7(2): 233-238. DOI:10.2527/JAS1948.72233X |
| [3] |
韩云珍, 洪渊, 薛永钦, 薛宏烽, 邱定杰, 王秀爱, 阮国荣. 美系大白猪VRTN和MC4R基因多态性及其与生长和胴体性状的关联分析[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2022, 54(12): 9-14. HAN Y Z, HONG Y, XUE Y Q, XUE H F, QIU D J, WANG X A, RUAN G R. Association between polymorphism of the VRTN and MC4R genes and the growth and carcass traits of American large white pigs[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 54(12): 9-14. |
| [4] |
刘倩, 岳静伟, 牛乃琪, 王立贤, 张龙超. VRTN和NR6A1基因的因果变异与北京黑猪脊椎数性状的关联分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57(S1): 218-221. DOI:10.19556/j.0258-7033.20210624-02 LIU Q, YUE J W, NIU N Q, WANG L X, ZHANG L C. Association between causal variation of VRTN and NR6A1 genes and vertebral number traits in Beijing black pigs[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57(S1): 218-221. DOI:10.19556/j.0258-7033.20210624-02 |
| [5] |
郝小静, 韩丽娟, 王彦平, 赵雪艳, 王继英. VRTN基因SINE插入突变与杜洛克肋骨数、胴体及肉质性状关联分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(5): 1216-1221. DOI:10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2022.5.030 HAO X J, HAN L J, WANG Y P, ZHAO X Y, WANG J Y. Association analysis of SINE insertion mutation in VRTN gene with number of ribs, carcass and meat auality traits in Duroc[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 35(5): 1216-1221. DOI:10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2022.5.030 |
| [6] |
庄站伟, 付帝生, 丁荣荣, 杨明, 李绍云, 吴珍芳, 杨杰, 郑恩琴. 美系杜洛克种猪体尺性状遗传参数估计及其与生长性状的关系研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 2018, 45(7): 121-125. DOI:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2018.07.020 ZHUANG Z W, FU D S, DING R R, YANG M, LI S Y, WU Z F, YANG J, ZHENG E Q. Estimation of genetic parameters of body measurements traits and the relationship with growth traits in an American Duroc population[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 45(7): 121-125. DOI:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2018.07.020 |
| [7] |
WADA Y, AKITA T, AWATA T, FURUKAWA T, SUGAI N, INAGE Y, ISHⅡ K, ITO Y, KOBAYASHI E, KUSUMOTO H, MATSUMOTO T, MIKAWA S, MIYAKE M, MURASE A, SHIMANUKI S, SUGIYAMA T, UCHIDA Y, YANAI S, YASUE H. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis in a Meishan x Göttingen cross population[J]. Animal Genetics, 2000, 31(6): 376-384. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2052.2000.00696.x |
| [8] |
MIKAWA S, HAYASHI T, NⅡ M, SHIMANUKI S, MOROZUMI T, AWATA T. Two quantitative trait loci on Sus scrofa chromosomes 1 and 7 affecting the number of vertebrae[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2005, 83(10): 2247-2254. DOI:10.2527/2005.83102247x |
| [9] |
IJIRI M, LAI Y C, KAWAGUCHI H, FUJIMOTO Y, MIURA N, MATSUO T, TANIMOTO A. NR6A1 Allelic frequencies as an index for both miniaturizing and increasing pig body size[J]. In Vivo, 2021, 35(1): 163-167. DOI:10.21873/invivo.12244 |
| [10] |
徐盼, 刘林雨, 仲德, 何鑫鑫, 罗阳琦文, 马政. 苏姜猪NR6A1和VRTN基因多态性及其与生产性状的关联分析[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2022, 54(4): 10-16. XU P, LIU L Y, ZHONG D, HE X X, LUO Y Q W, MA Z. Association between polymorphism of NR6A1 and VRTN genes and production traits in Sujiang pigs[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 54(4): 10-16. |
| [11] |
MIKAWA S, SATO S, NⅡ M, MOROZUMI T, YOSHIOKA G, IMAEDA N, YAMAGUCHI T, HAYASHI T, AWATA T. Identification of a second gene associated with variation in vertebral number in domestic pigs[J]. BMC Genetics, 2011, 12: 5-17. DOI:10.1186/1471-2156-12-5 |
| [12] |
DUAN Y, ZHANG H, ZHANG Z, GAO J, YANG J, WU Z, FAN Y, XING Y, LI L, XIAO S, HOU Y, REN J, HUANG L. VRTN is required for the development of thoracic vertebrae in mammals[J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2018, 14(6): 667-681. DOI:10.7150/ijbs.23815 |
| [13] |
BURGOS C, LATORRE P, ALTARRIBA J, CARRODEGUAS J, VARONA L, LÓPEZ-BUESA P. Allelic frequencies of NR6A1 and VRTN, two genes that affect vertebrae number in diverse pig breeds: A study of the effects of the VRTN insertion on phenotypic traits of a Duroc×Landrace-Large White cross[J]. Meat Science, 2015, 100: 150-155. DOI:10.1016/j.meatsci.2014.09.143 |
| [14] |
FAN Y, XING Y, ZHANG Z, AI H, OUYANG Z, OUYANG J, YANG M, LI P, CHEN Y, GAO J, LI L, HUANG L, REN J. A further look at porcine chromosome 7 reveals VRTN variants associated with vertebral number in Chinese and Western pigs[J]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(4): e62534. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0062534 |
| [15] |
王可甜, 柴捷, 张凤鸣, 郭宗义, 张波. 猪胴体性状测定方法与技巧[J]. 畜禽业, 2022, 33(12): 21-23. DOI:10.19567/j.cnki.1008-0414.2022.12.007 WANG K T, CHAI J, ZHANG F M, GUO Z Y, ZHANG B. Methods and techniques for determining pig carcass traits[J]. Livestock and Poultry Industry, 2022, 33(12): 21-23. DOI:10.19567/j.cnki.1008-0414.2022.12.007 |
| [16] |
郭建凤, 王诚, 王彦平, 赵雪艳, 刘畅, 蔺海朝. 采食不同饲料试验猪肉质性状比较及运输、宰前应激对其血液生化指标的影响[J]. 养猪, 2018(4): 49-53. DOI:10.13257/j.cnki.21-1104/s.2018.04.019 GUO J F, WANG C, WANG Y P, ZHAO X Y, LIU C, LIN H C. Comparison of pork quality traits and effects of transportation and pre-slaughter stress on blood biochemical indexes in different feed intake tests[J]. Swine Production, 2018(4): 49-53. DOI:10.13257/j.cnki.21-1104/s.2018.04.019 |
| [17] |
王圣楠, 邵勇钢, 卢元鹏, 单保森, 韦伟, 陈杰, 张立凡. 猪肉质性状评定方法及其研究进展[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2020, 52(1): 148-151. WANG S N, SHAO Y G, LU Y P, SHAN B S, WEI W, CHEN J, ZHANG L F. Methods for evaluating pork quality traits and progress in research on the methods[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 52(1): 148-151. |
| [18] |
廖印长, 高虎, 张跃博, 殷诗舒, 徐康, 何俊. 宁乡猪宰后pH和肉色性状的全基因组关联分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57(S1): 174-181. DOI:10.19556/j.0258-7033.20210630-08 LIAO Y C, GAO H, ZHANG Y B, YIN S S, XU K, HE J. Genome-wide association analysis of post-slaughter pH and flesh color traits of pigs in Ningxiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57(S1): 174-181. DOI:10.19556/j.0258-7033.20210630-08 |
| [19] |
袁仁强, 陈瑶生, 刘小红. 广东省生猪产业发展历史演变、问题与对策[J]. 广东农业科学, 2022, 49(5): 142-149. DOI:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2022.05.017 YUAN R Q, CHEN Y S, LIU X H. Historical evolution, problems and countermeasures in development of Guangdong pig industry[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 49(5): 142-149. DOI:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2022.05.017 |
| [20] |
王塑天, 孟繁明, 李剑豪. 广东猪种质资源利用与育种生物技术创新[J]. 广东农业科学, 2020, 47(12): 134-143. DOI:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2020.12.014 WANG S T, MENG F M, LI J H. Utilization of porcine germplasm resources in Guangdong and innovation of breeding biotechnology[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 47(12): 134-143. DOI:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2020.12.014 |
| [21] |
卢世豪, 崔浩, 闫耀晖, 孙晓梅, 李清春, 陈鑫, 祁梦凡, 何凡, 黎明国, 黄涛. VRTN基因型对猪生长和繁殖性能的影响[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 40(4): 460-465. DOI:10.13880/j.cnki.65-1174/n.2022.22.019 LU S H, CUI H, YAN Y H, SUN X M, LI Q C, CHEN X, QI M F, HE F, LI M G, HUANG T. Association of VRTN gene polymorphisms with growth and reproductive trait in pig[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2022, 40(4): 460-465. DOI:10.13880/j.cnki.65-1174/n.2022.22.019 |
| [22] |
HIROSE K, MIKAWA S, OKUMURA N, NOGUCHI G, FUKAWA K, KANAYA N, MIKAWA A, ARAKAWA A, ITO T, HAYASHI Y, TACHIBANA F, AWATA T. Association of swine vertnin (VRTN) gene with production traits in Duroc pigs improved using a closed nucleus breeding system[J]. Animal Science Journal, 2013, 84(3): 213-221. DOI:10.1111/j.1740-0929.2012.01066.x |
| [23] |
张慧. 解析VRTN基因因果突变调控猪胸椎数的分子机理[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2018. ZHANG H. Unravelling the molecular mechanism of VRTN causative mutations for thoracic vertebral number in pigs[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2018. |
| [24] |
VAN SON M, LOPES M S, MARTELL H J, DERKS M F L, GANGSEI L E, KONGSRO J, WASS M N, GRINDFLEK E H, HARLIZIUS B. A QTL for number of teats shows breed specific effects on number of vertebrae in pigs: bridging the gap between molecular and quantitative genetics[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2019, 10: 272-288. DOI:10.3389/fgene.2019.00272 |
| [25] |
范寅. 鉴别猪7号染色体影响脊椎数变异的因果突变位点[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2014. FAN Y. ldentifieation of the causative mutation underlying the QTL for vertebral numbers on pig chromosome 7[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2014. |
| [26] |
JIANG N, LIU C, LAN T, ZHANG Q, CAO Y, PU G, NIU P, ZHANG Z, LI Q, ZHOU J, LI X, HOU L, HUANG R, LI P. Polymorphism of VRTN gene g.20311_20312ins291 was associated with the number of ribs, carcass diagonal length and cannon bone circumference in Suhuai pigs[J]. Animals, 2020, 10(3): 484-493. DOI:10.3390/ani10030484 |
| [27] |
NAKANO H, SATO S, UEMOTO Y, KIKUCHI T, SHIBATA T, KADOWAKI H, KOBAYASHI E, SUZUKI K. Effect of VRTN gene polymorphisms on Duroc pig production and carcass traits, and their genetic relationships[J]. Animal Science Journal, 2015, 86(2): 125-131. DOI:10.1111/asj.12260 |
| [28] |
HUANG J, ZHANG M, YE R, MA Y, LEI C. Effects of increased vertebral number on carcass weight in PIC pigs[J]. Animal Science Journal, 2017, 88(12): 2057-2062. DOI:10.1111/asj.12881 |
| [29] |
ZHANG L C, YUE J W, PU L, WANG L G, LIU X, LIANG J, YAN H, ZHAO K B, LI N, SHI H B, ZHANG Y B, WANG L X. Genome-wide study refines the quantitative trait locus for number of ribs in a Large White×Minzhu intercross pig population and reveals a new candidate gene[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2016, 291(5): 1885-1890. DOI:10.1007/s00438-016-1220-1 |
| [30] |
LI L Y, XIAO S J, TU J M, ZHANG Z K, ZHENG H, HUANG L B, HUANG Z Y, YAN M, LIU X D, GUO Y M. A further survey of the quantitative trait loci affecting swine body size and carcass traits in five related pig populations[J]. Animal Genetics, 2021, 52(5): 621-632. DOI:10.1111/age.13112 |
| [31] |
YANG J, HUANG L, YANG M, FAN Y, LI L, FANG S, DENG W, CUI L, ZHANG Z, AI H, WU Z, GAO J, REN J. Possible introgression of the VRTN mutation increasing vertebral number, carcass length and teat number from Chinese pigs into European pigs[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 19240-19247. DOI:10.1038/srep19240 |
(责任编辑 崔建勋)
 2023, Vol. 50
2023, Vol. 50